Interview 1/3: Kate Lycock of DW Radio’s Inside Europe interviewed me yesterday, on the historical role of fuel-denial in war, and the impacts of Ukraine’s drone strategy on Russia (first story, on 21 March)
Aside from some WW2 history, I identified two separate impacts we can see in the present Ukrainian campaign: a) The impact on Russian fuel deliveries to the war zones themselves and to the domestic Russian war economy, and b) their possible impact as a “force multiplier” for the oil-price cap sanctions on Russian oil exports, designed to deny Moscow its all-important oil revenues that are financing its aggression. I also speculated a bit as to how these strikes, together with Black Sea sea-drone operations, might be shaping coming Ukrainian offensive(s). (This show is also syndicated in the USA as I recall.)
2/3: on 20 March, I was also interviewed on the drone strikes by Voice of America’s Harry Ridgwell, while I was at the Berlin Energy Transition Dialogue, held at the German Federal Foreign Office. (See Video in LHS column.)
3/3: Lastly, I was quoted a couple times by Brendan Cole of the USA national magazine, Newsweek, on 18 March:
Read more: My DW, VoA & Newsweek interviews: “Ukrainian drones cripple Russian refineries.” Thoughts on strategy, impacts and historyRussia Faces ‘Serious’ Threat as Ukraine Attacks Refineries
Mar 18, 2024. By Brendan Cole, Senior News Reporter. You can read it HERE.
Note, there are new developments since yesterday, including Russia’s revenge strikes on Ukrainian infrastructure (reports are that 1 million Ukrainians have no electricity today) and on its Special Operations Headquarters. However, of the 30 Russian drones that swarmed to target this Kyiv building, every one was shot down.
Also, there are reports (Financial Times) that the USA is warning Ukraine that the strikes will draw retaliation and raise the price of oil.
Who cares! This has gone on for simply too long. There are vastly sufficient oil reserves in the world that can be tapped to fully replace Russian oil even if it were totally taken offline. After over two years of war, Washington and the EU Members should have by now begun a concerted effort to get sufficient new oil on line to enable blocking a high percentage of Russian exports from being exported to the world market
I talk about one possible approach to this in my DW interview, involving Denmark and Sweden inspecting and banning passage of sketchy Russian tankers through their economic zones in the Baltic Sea.
After two-plus years of war, there is no excuse to still be playing around with the oil price cap without either significantly lowing it — say, to $30/barrel as the Ukrainians suggest, in any case begin stepwise lowering it below the present $60, which would be a signal to producers to start developing new fields — and/or finding ways to block shipments more directly.
This is not to diminish the clever and difficult work people at especially OFAC and the USA Justice Department in Washington and their colleagues in London and Brussels have carried out to tighten and make more effective the oil price cap. However, as it stands, the cap is too high and a weak instrument.
The entire political preoccupation with keeping Russian oil on the market is fundamentally flawed, Signals must be given to the market that it will be step-wise taken off the market, which will instill/stimulate IOCs, NOCs and smaller firms to rapidly bring undeveloped oil reserves online to permanently replace Russian exports.
LAST: Here are some references for further reading that I found useful in my research.
- Highly recommended, by my friend, the intrepid Михайло Гончар – Україна уразила вже третину найбільших російських НПЗ – Главред https://glavred.net/article/v-rossii-krasivo-gorit-ukraina-porazila-uzhe-tret-krupneyshih-rossiyskih-npz-gonchar-10550015.html (Translation: Russia is on fire: Ukraine has already hit a third of the largest Russian refineries – Interview with Michael Gonchar, March 14, 2024, 4:02 p.m, Ukrainian drones are reducing oil refining in Russia and creating a fuel shortage there, Mykhailo Gonchar believes.)
- Ukraine Drone Strike Hits Refining Complex Deep in Russia || Peter Zeihan – YouTube (NOTE: added a gap to URL before ‘.com’ to prevent it displaying here) https://www.youtube .com/watch?v=86YrV2D-nB4
- Ukraine’s Drones Threaten Russian Oil Industry With Refinery Strikes – Bloomberg https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2024-03-20/ukraine-s-drones-threaten-russian-oil-industry-with-refinery-strikes
- Ukraine’s Drones Threaten Russian Oil Industry With Refinery Strikes – Bloomberg https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2024-03-20/ukraine-s-drones-threaten-russian-oil-industry-with-refinery-strikes
- Russian refineries targeted by Ukraine’s drones | Reuters https://www.reuters.com/business/energy/russian-refineries-targeted-by-ukraines-drones-2024-03-18/
- Ukraine’s SBU Said Behind Massive Attacks On Russian Oil Refineries https://www.rferl.org/a/ukraine-russia-air-strikes/32859724.html
- Damaged refining capacity drives up Russia’s gasoline, diesel prices | Reuters https://www.reuters.com/markets/commodities/damaged-refining-capacity-drives-up-russias-gasoline-diesel-prices-2024-03-19/




 My Wikistrat webinar transcript “Oil Price War & COVID” from a couple weeks ago is
My Wikistrat webinar transcript “Oil Price War & COVID” from a couple weeks ago is 
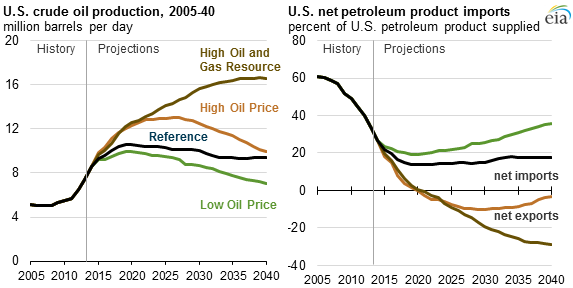 Contrary to his campaign hype (see article below), Trump-as-president will not do anything to interfere with the free flow of oil or gas to or from the USA. As I pointed out in the Investors Business Daily interview (Gillian Rich’s story is below), people central to Trump’s administration – such as Rex Tillerson, his designated secretary of state and former CEO of Exxon, and Harold Hamm, Trump’s fracking billionaire friend he wanted for secretary of energy – are global-market-oriented businessmen who would never agree to disconnect the USA from global energy markets.
Contrary to his campaign hype (see article below), Trump-as-president will not do anything to interfere with the free flow of oil or gas to or from the USA. As I pointed out in the Investors Business Daily interview (Gillian Rich’s story is below), people central to Trump’s administration – such as Rex Tillerson, his designated secretary of state and former CEO of Exxon, and Harold Hamm, Trump’s fracking billionaire friend he wanted for secretary of energy – are global-market-oriented businessmen who would never agree to disconnect the USA from global energy markets.



