This slideshow requires JavaScript.
The “Oil Price War of 2020” was launched at the worst possible time. The COVID-19 pandemic was spreading to the world beyond China, promising to kill tens-of-thousands, and bring a global economic collapse.
However, this war was not preordained. Things could have gone otherwise from the start. It was a decision, a sort of Pearl-Harbor-esque surprise attack, announced by Russian minister of energy, Alexander Novak, upon his arriving late to the OPEC-plus summit hall in Vienna on March 6.
If Moscow now abandons its all-out war on US shale, it will be because Putin has miscalculated. He was willing to increase the pain for everyone else by exploiting the COVID-19 energy crisis in a half-baked attempt to get out from under the US sanctions. However, the unanticipated repercussions might get too hot for Moscow.
The facts about why Putin decided to launch this oil price war are important to decode. A key aspect to understand is that Moscow’s game plan was to blame the Saudis; and it soon began a disinformation campaign saying the Saudis launched the war.
We shall see, below and in future posts, how this blame-shifting is a stratagem designed to manipulate a section of US politicians and especially independent US oil producers, who traditionally hold strong, anti-Saudi sentiments (to be clear: they have good reasons to hold these anti-Saudi views), to preferentially sympathize with Russia against the Saudis and to lobby Trump and Congress to give Moscow relief from US sanctions.
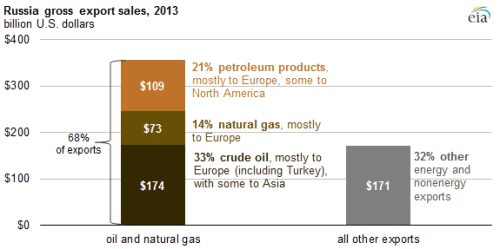
Whether this Oil War strategy of Moscow can, at least in part, succeed in freeing Russia from US sanctions is not clear. But, Moscow’s is highly motivated to succeed due to the significant constraints these sanctions are imposing on Russia. They include sanctions in retaliation for its war against Ukraine, since 2014, which have undermined expansion of Russia’s domestic oil and gas sector; sanctions which have stalled Russian-German plans to finish the Nord Stream 2 pipeline; and sanctions on Rosneft’s efforts to sustain the Maduro dictatorship in Venezuela.
Today, as explained below, I would say the odds are against Moscow’s success, with the plan bordering on adventurism. The Saudi’s initial response, in so far as it specifically targets Russia’s oil business, is rational; however, by de facto joining the Russian oil price war on US shale, the Saudis will also provoke a backlash from powerful US oil-business and political interests, which is likely precisely what Putin and Igor Sechin hoped to bait the Saudis’ Prince MbS into doing.
Considering the pain the world is already suffering, Putin and Sechin’s callous game to exploit the COVID-19 oil-market crisis must be seen for what it is. Most especially, one should not acquiesce to Moscow’s disinformation campaign to shift the blame elsewhere.
In Vienna: Who started the price war?
For weeks, Riyadh had aggressively lobbied the 10 OPEC and 11 non-OPEC members of the OPEC-plus alliance to agree to a major production cut. This alliance had been born in 2016, of a newfound, market-dictated, yet grudging, Russian-Saudi mutual recognition of the reality that only such a large-scale collective effort could begin to get control of a market in long-term oversupply. By December 2019, their OPEC-plus group had Continue reading →


 My Wikistrat webinar transcript “Oil Price War & COVID” from a couple weeks ago is
My Wikistrat webinar transcript “Oil Price War & COVID” from a couple weeks ago is 


 What are US experts’ and officials’ views on the increasingly conflictive energy and geostrategic relations between Russia, Germany, Poland and Ukraine?
What are US experts’ and officials’ views on the increasingly conflictive energy and geostrategic relations between Russia, Germany, Poland and Ukraine? 





 00
00 I was interviewed by Matt Egan of CNNMoney. Three points, if I may:
I was interviewed by Matt Egan of CNNMoney. Three points, if I may: Here`s my latest at Berlin Policy Journal: about OPEC`s 30 Novermber meeting, US shale and the geopolitics from the Trump Administration towards Iran and the Saudis. – Tom O`D.
Here`s my latest at Berlin Policy Journal: about OPEC`s 30 Novermber meeting, US shale and the geopolitics from the Trump Administration towards Iran and the Saudis. – Tom O`D.